A Transistor is an electronic component created by joining two types of semiconductors. One type of semiconductor is "P-type" and the other is "N-type". The two types of bipolar-junction transistors (BJTs) that result are explained below.
1) A P-type region lies between 2 N-Typed Semi Conductors . This kind of configuration is called NPN Transistor.
2) An N-type region lies between 2 P-Typed Semi Conductors . This kind of configuration is called PNP Transistor.
It is equivalent to two nose-to-nose diodes, but as before, just connecting two diodes will not work. Generally, a PNP diode is identical to an NPN diode, but with all currents reversed.
Bipolar transistors have 3 terminals : Base, Collector, Emitter
Transistors are commonly used in amplification, switching, and buffering signals or applied voltages.
Operating Modes[edit]
A bipolar transistor can be regarded as a current amplifier. The (small) base current is amplified by a factor (typically in the range of 10 to 500) to yield a proportionally larger collector current. But in order for a transistor to perform its task properly, there have to be voltages applied to make the transistor conduct current. These voltages are called bias voltages.
Depending on how the transistor is used, it can behave as a (relatively) linear amplifier or a switch.
A bipolar transistor has three terminals, base, emitter and collector, and two internal PN-junctions; the collector to base junction (CBJ) and the emitter to base junction (EBJ). A junction is conducting a significant amount of current in the forward direction (P to N) if the voltage across it is larger than a diode forward voltage drop (Vd), which is around 0.6 V in silicon. The operation of the transistor is largley affected by how the terminals are biased. The table below shows how to bias the base-emitter voltage (Vbe) and the collector-emitter voltage (Vce) to bring the transistor into the different modes. The table shows the voltages for a silicon NPN transistor:
| Operating Mode | Vbe | Vce |
|---|---|---|
| Active | Vd | Vcesat |
| Cut-Off |
 The field-effect transistor (FET) is a transistor that uses an electric field to control the shape and hence the conductivity of a channel of one type of charge carrier in a semiconductor material. FETs are sometimes called unipolar transistors to contrast their...
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a transistor that uses an electric field to control the shape and hence the conductivity of a channel of one type of charge carrier in a semiconductor material. FETs are sometimes called unipolar transistors to contrast their...
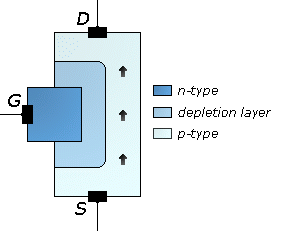 The junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET or JUGFET) is the simplest type of field-effect transistor. It can be used as an electronically-controlled switch or as a voltage-controlled resistance. Electric charge flows through a semiconducting channel between...
The junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET or JUGFET) is the simplest type of field-effect transistor. It can be used as an electronically-controlled switch or as a voltage-controlled resistance. Electric charge flows through a semiconducting channel between...